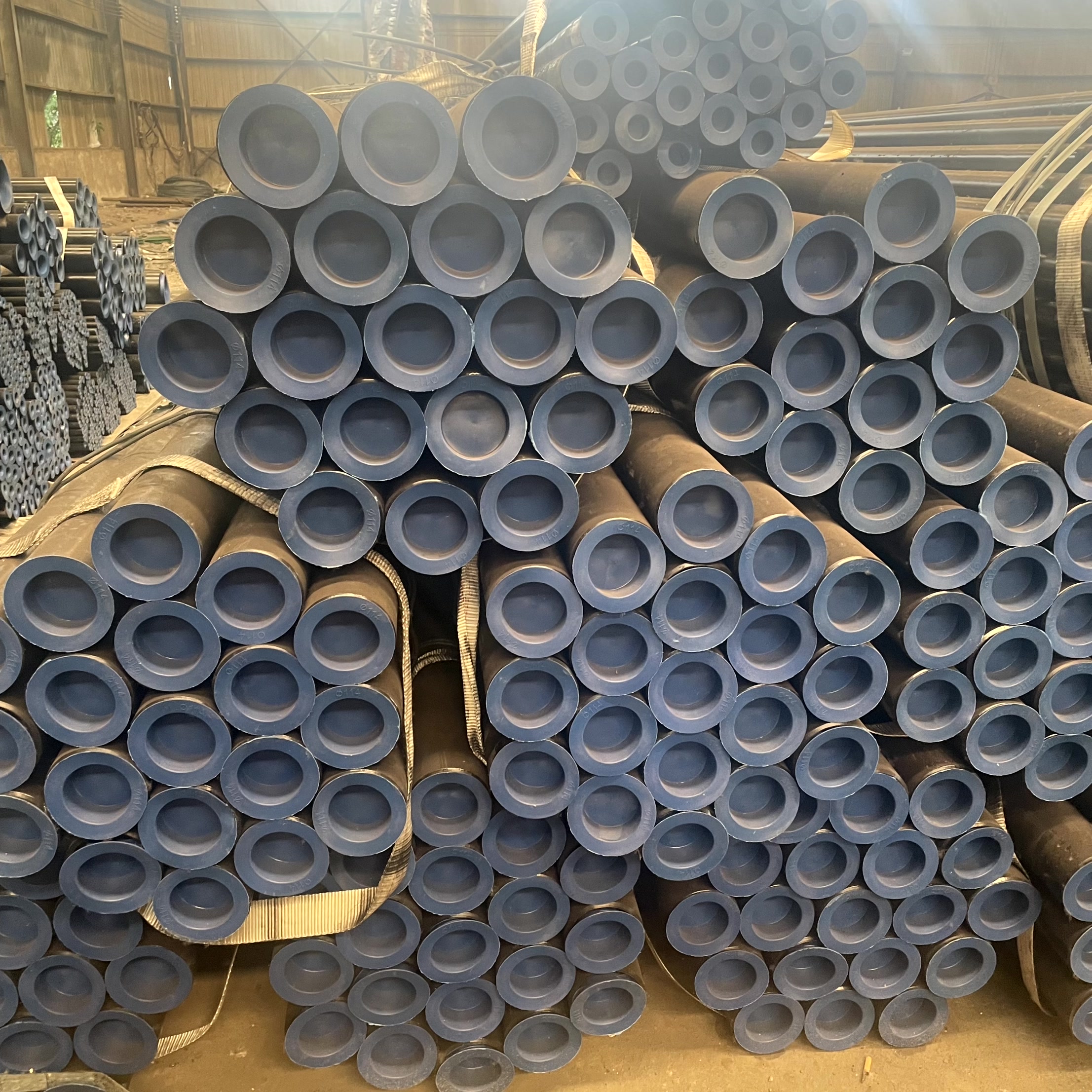
I. Introduction: The World of Stainless Steel Beyond the Basics
-
Start by acknowledging the ubiquitous presence and importance of stainless steel in modern industry, highlighting its primary benefit: corrosion resistance.
-
Reiterate that while SUS304 (or its ASTM equivalent, 304) is the most well-known "workhorse," it's just one of many stainless steel grades.
-
Emphasize that selecting the correct grade is paramount; a mismatch can lead to premature failure and significant costs.
-
Outline the article's goal: to demystify stainless steel grades like SUS304, exploring their classifications, key characteristics, and application suitability, helping professionals make informed material selections.
II. The Fundamentals: Understanding Stainless Steel Classifications
-
Briefly explain what makes steel "stainless" (min. 10.5% Chromium).
-
Introduce the five main families of stainless steel, highlighting their general characteristics:
-
Austenitic Stainless Steels: (e.g., 300 series like 304, 316) - Most common, non-magnetic, excellent corrosion resistance, weldability, ductility.
-
Ferritic Stainless Steels: (e.g., 400 series like 430) - Magnetic, good corrosion resistance (but less than austenitic), lower cost, often used in automotive/architectural.
-
Martensitic Stainless Steels: (e.g., 400 series like 410) - Magnetic, harder, can be heat-treated for high strength, less corrosion resistant.
-
Duplex Stainless Steels: (e.g., 2205, 2507) - Mix of austenitic and ferritic, very high strength, superior corrosion resistance (especially stress corrosion cracking).
-
Precipitation Hardening (PH) Stainless Steels: (e.g., 17-4 PH) - Achieve very high strength through heat treatment.
-
III. The Austenite Dominance: In-depth Look at Common Grades (Like SUS304)
-
3.1. SUS304 / 304 Stainless Steel (The Standard Benchmark):
-
Composition: 18% Chromium, 8% Nickel (the "18/8" grade).
-
Properties: Excellent general corrosion resistance in atmospheric and mild chemical environments, superb weldability and formability, non-magnetic.
-
Applications: Food processing, kitchen equipment, architectural trim, general chemical applications, non-chlorinated water lines.
-
Keywords: SUS304 stainless steel, 304 stainless steel, 18/8 grade, general purpose stainless
-
-
3.2. SUS316 / 316L Stainless Steel (The Chloride Champion):
-
Composition: Similar to 304, but with the crucial addition of Molybdenum (2-3%). "L" denotes low carbon.
-
Properties: Significantly enhanced resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion, especially in chloride-rich environments (e.g., seawater, brine, acidic solutions). Improved strength at elevated temperatures.
-
Applications: Marine environments, chemical processing (acids), pharmaceutical equipment, medical implants, outdoor architectural in coastal areas.
-
Keywords: SUS316 stainless steel, 316L stainless steel, molybdenum, marine grade stainless, chloride resistance
-
-
3.3. SUS321 / 321 Stainless Steel (The High-Temperature Stabilizer):
-
Composition: Similar to 304, but with the addition of Titanium.
-
Properties: Excellent resistance to intergranular corrosion after exposure to temperatures in the carbide precipitation range (425-850°C), making it suitable for high-temperature welding applications without subsequent annealing.
-
Applications: Aircraft exhaust manifolds, boiler tubes, heat exchangers, expansion bellows, high-temperature chemical process equipment.
-
Keywords: SUS321 stainless steel, 321 stainless steel, high temperature stainless, intergranular corrosion
-
IV. Other Notable Stainless Steel Grades for Specific Needs
-
4.1. Ferritic Grades (e.g., SUS430 / 430 Stainless Steel):
-
Composition: High Chromium (17%), no Nickel.
-
Properties: Magnetic, good corrosion resistance (less than 304), lower cost, good formability.
-
Applications: Kitchen appliances (non-critical parts), automotive trim, architectural panels, where appearance and cost are key, and corrosion is mild.
-
Keywords: SUS430 stainless steel, 430 stainless steel, ferritic stainless, cost-effective stainless
-
-
4.2. Duplex Stainless Steels (e.g., 2205, 2507):
-
Composition: Balanced Chromium, Nickel, Molybdenum, and Nitrogen.
-
Properties: Combine the best properties of austenitic and ferritic grades: very high strength (double that of 304/316), superior resistance to stress corrosion cracking and pitting/crevice corrosion.
-
Applications: Oil and gas industry (offshore platforms, pipelines), chemical tankers, pulp and paper industry, structural applications requiring extreme strength and corrosion resistance.
-
Keywords: duplex stainless steel, 2205 stainless, high strength stainless, stress corrosion cracking resistance
-
V. Choosing the Right Grade: Key Selection Factors
-
Corrosive Environment: Is it atmospheric, acidic, alkaline, or chloride-rich? This is the primary driver.
-
Temperature: Operating temperature range (ambient, elevated, cryogenic).
-
Pressure & Strength: Required mechanical strength, yield, and tensile properties.
-
Fabrication Requirements: Weldability, formability, machinability.
-
Cost vs. Performance: Balancing initial material cost with long-term performance, maintenance, and replacement costs.
-
Regulatory & Industry Standards: Compliance with ASTM, API, EN, JIS, etc.
VI. Conclusion: Strategic Material Selection for Long-Term Success
-
Reiterate that while stainless steel grades like SUS304 serve as excellent general-purpose solutions, understanding the broader spectrum of stainless steel grades is essential for optimizing industrial applications.
-
Emphasize that a careful consideration of the operating environment, mechanical demands, and cost factors, beyond just basic corrosion resistance, is crucial for selecting the ideal material.
-
Stress that investing in the right stainless steel grade upfront prevents costly failures, enhances operational safety, and extends the lifespan of critical infrastructure.
-
CTA (Call to Action): Consult our material specialists for expert guidance on selecting the perfect stainless steel pipe grade for your unique project challenges!