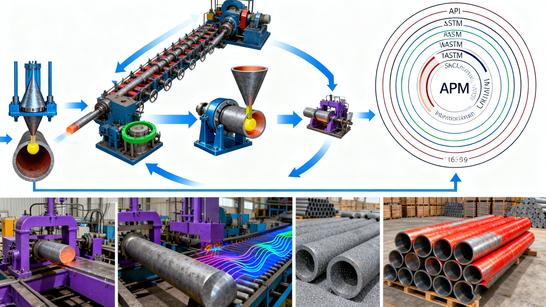
1. Introduction: What Is a Seamless Steel Pipe?
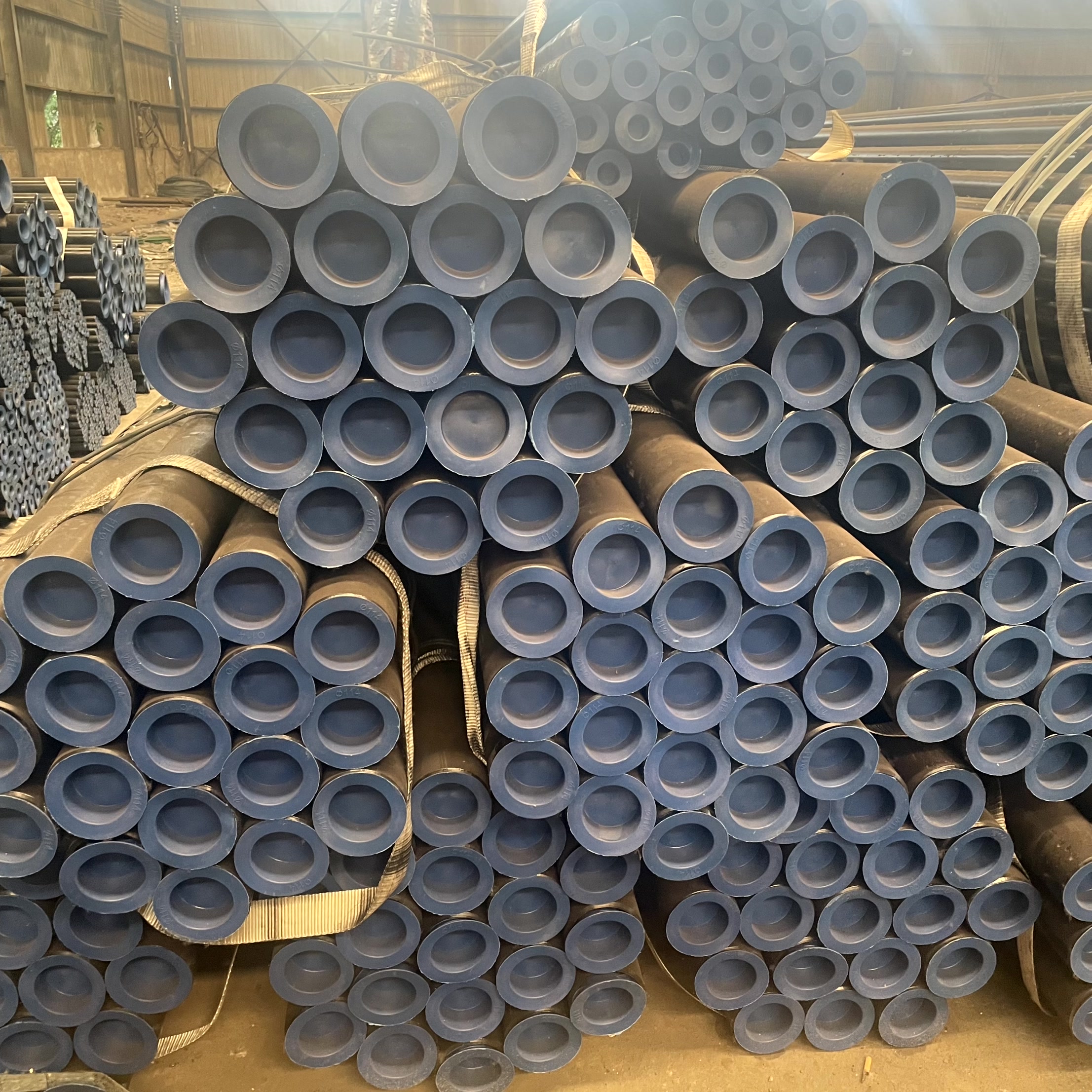
Seamless steel pipes are the backbone of modern industrial infrastructure, providing reliable and high-pressure fluid conveyance across the globe. Unlike welded pipes, which are manufactured by rolling and welding steel plates, seamless steel pipes are characterized by having no welded seam across their length. They are produced from a solid steel billet (round bar) that is heated and then pierced to form a hollow tube.
This unique, monolithic structure provides superior strength, uniform wall thickness, and exceptional resistance to internal pressure, making them the preferred choice for critical applications involving high temperatures, high pressures, and corrosive environments, such as those found in the oil, gas, power generation, and chemical industries.
2. Key Manufacturing Methods (Hot Rolled vs Cold Drawn)
The manufacturing process is the defining factor for the pipe's final properties and quality. While both methods start with the piercing of a solid billet, the subsequent steps differentiate the product significantly. For a detailed breakdown, please see the cluster article: 【How Seamless Steel Pipes Are Manufactured: From Billet to Finished Tube】
2.1. Hot Rolled Seamless Pipes
-
Process: After the billet is pierced, the resulting hollow shell is further rolled and sized while the material is still above its recrystallization temperature (typically over 1700℉).
-
Characteristics: High production speed, thicker walls, larger diameters, and a slightly rougher surface finish. They are primarily used in high-temperature, high-pressure, and structural applications where precise dimensional tolerance is less critical.
-
Key Phrase: Hot rolled seamless pipe
2.2. Cold Drawn Seamless Pipes
-
Process: Pipes are produced from hot-rolled mother tubes that are acid pickled and then drawn through a die and mandrel at room temperature.
-
Characteristics: Excellent dimensional accuracy, smoother surface, thinner walls, and improved mechanical properties due to work hardening. Often referred to as precision pipes. These are suitable for high-precision components like seamless tube for delivery cylinder applications.
-
Key Phrase: Cold drawn tube
For a direct comparison and selection guidance, refer to: 【Hot Rolled vs Cold Drawn Seamless Pipes: Key Differences and Selection Guide】
3. Main Standards: ASTM A106, A53, API 5L, DIN 17175
The application of a seamless pipe dictates which international standard it must adhere to. These standards specify the chemical composition, mechanical properties, dimensions, testing methods, and delivery conditions.
| Standard | Primary Application | Key Grades |
| ASTM A106/A53 | High-temperature service (A106) and general fluid service (A53). | A, B, C |
| API 5L | Line pipe for transporting gas, water, and oil. | Gr. B, X42, X52 to X80 |
| DIN 17175/EN 10216 | Boiler and pressure vessel applications (European standard). | 10CrMo910, P235GH |
Understanding the nuances of each is vital for project integrity.
-
In-depth on US standards: 【Understanding ASTM A106/A53 Seamless Steel Pipes: Grades A, B, and C Explained】
-
Focus on oil and gas standards: 【API 5L Seamless Line Pipe: PSL1 vs PSL2 Standards Explained】
-
European pressure standards: 【DIN 17175 & EN 10216 Standards for Boiler and Pressure Seamless Pipes】
4. Material Grades and Chemical Composition
The majority of seamless pipes are manufactured from carbon steel pipe or low-alloy steel. The grade (e.g., Grade B in A106/A53) denotes specific limits for elements like Carbon (C), Manganese (Mn), Silicon (Si), and trace elements like Sulfur (S) and Phosphorus (P). The precise chemical composition determines the steel's weldability, strength, and corrosion resistance.
| Element | ASTM A106 Gr. B (Max %) | API 5L Gr. B (Max %) |
| Carbon (C) | 0.30 | 0.28 |
| Manganese (Mn) | 0.29–1.06 | 1.20 |
| Sulfur (S) | 0.035 | 0.030 |
| Phosphorus (P) | 0.035 | 0.030 |
Note: The mechanical strength is proportional to the Carbon and Manganese content, within the standard’s limits.
While the chemical composition dictates the potential performance of the steel, the actual realization of its mechanical properties—such as meeting the required yield strength for API 5L or Grade C of A106—is achieved through precise thermal manipulation.
【Heat Treatment in Seamless Pipe Production: Normalizing, Annealing, and Quenching】
5. Inspection & Testing Requirements
Quality control is paramount for safety-critical pipelines. All certified seamless pipes must undergo rigorous testing to ensure conformance. This typically includes:
-
Tensile and Yield Strength Tests: To measure mechanical performance.
-
Chemical Analysis: To verify material composition.
-
Flattening and Bending Tests: To assess ductility.
-
Hydrostatic Testing: The pipe is filled with water and pressurized to a specified level to check for leaks and structural integrity.
-
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Methods like Ultrasonic Testing and Eddy Current Testing are used to detect internal and external defects without compromising the pipe.
To understand the specifics of defect detection, read: 【Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) Methods for Seamless Pipes】
6. Typical Applications in Oil, Gas, and Structural Industries
Seamless pipes are indispensable across various sectors due to their strength and reliability.
6.1. Oil and Gas (O&G)
This is the largest consumer market. Seamless pipes are used as line pipe for transporting crude oil and natural gas over long distances, as well as casing and tubing in the drilling and extraction process. The required standards here are often API 5L (for line pipe) and API 5CT (for casing/tubing).
For case studies and detailed applications: 【Applications of Seamless Steel Pipes in Oil & Gas Industry】
6.2. Power Generation
Seamless pipes are used in boilers, superheaters, and heat exchangers within power plants (fossil fuel and nuclear), where high-temperature steam and water conveyance demand extreme reliability.
6.3. Mechanical and Structural Engineering
Precision cold-drawn tubes are critical for hydraulic cylinders, automotive components, and various machinery parts, demanding tight tolerance and smooth finishes. Seamless pipes are also used as structural supports where high load-bearing capacity is required.
More on these non-fluid applications: 【Seamless Pipes for Mechanical and Structural Engineering】
7. Comparison with Welded Steel Pipes
The core difference lies in their manufacturing method and resulting performance.
| Feature | Seamless Pipe | Welded Pipe |
| Structure | Monolithic (No seam) | Has a welded seam |
| Pressure Resistance | Excellent (Higher Rating) | Good (Lower Rating) |
| Wall Uniformity | Excellent | Can be slightly uneven at the seam |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Ideal Use | High-pressure, high-temp, critical service | Low-pressure, general structural, large diameter |
Seamless pipe is always specified for critical applications where the failure of a seam is unacceptable.
8. Global Market and Export Trends
The seamless pipe market is directly tied to the global energy sector's capital expenditure and new pipeline projects. Demand for high-grade API 5L pipes remains strong in developing O&G regions. There is a growing focus on sustainability, with buyers increasingly looking for sustainable steel production methods from manufacturers. The competitive landscape for the flange market and the pipe flange market is also interlinked, as high-quality seamless pipes require matching high-quality flange material and fittings.
For a forward-looking analysis of the industry: 【Global Seamless Steel Pipe Market Outlook 2025–2030】
9. Choosing the Right Seamless Pipe for Your Project: A Buyer’s Guide
Selecting the right pipe involves a careful match of project needs to pipe specifications:
-
Determine Application & Standard: (e.g., High-pressure line pipe $\rightarrow$ API 5L PSL2).
-
Specify Dimensions: Outer Diameter (OD) and Wall Thickness (WT).
-
Select Material Grade: Based on required strength (e.g., Gr. B, X52, etc.).
-
Confirm Testing Needs: Ensure Hydrostatic, NDT, and specific mechanical tests are documented.
-
Evaluate Supplier Capacity: Check certifications (ISO, API), quality control processes, and export experience.
10. FAQ About Seamless Pipes
Q: What is the most common seamless pipe material?
A: Carbon steel, particularly conforming to ASTM A106 Grade B and API 5L Grade B.
Q: Why are seamless pipes generally more expensive than welded pipes?
A: The manufacturing process, which involves piercing a solid billet and the need for high-quality raw materials and specialized equipment (piercing mills), is inherently more complex and costly than plate rolling and welding.
As a professional seamless steel pipe manufacturer, Hebei Cangtie provides high-quality ASTM A106/API 5L pipes with strict quality inspection and export packaging. We encourage you to reach out to our team for custom seamless pipe solutions that perfectly match your project’s demanding specifications.